前言
閉著眼睛學東西最困擾的是資料很多,但是完全不知道怎麼從那邊下手。這次運氣很好終於找到大大推荐的入門教材: Discovering the STM32 Microcontroller 作為一個突破點。雖然他上面講的是STM32F1,不過改一下還是可以在開發版上面動,短期內的自學大概會以這本書為主。
本篇文章主要是介紹在GNU/Linux下的STM32F429 開發軟體,這次以LED閃滅為實習題目,以後的實習會基於這次的專案為主。有興趣的朋友請自行到我的Github repository 取用。注意是這個專案單純自爽,常常會git push -f變動commit,如果有人fork我再調整。
目錄
測試環境
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
$ lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 14.04.4 LTS
Release: 14.04
Codename: trusty
$ arm-none-eabi-gcc --version
arm-none-eabi-gcc (GNU Tools for ARM Embedded Processors) 5.4.1 20160609 (release) [ARM/embedded-5-branch revision 237715]
...
SPL版本: STM32F4xx_DSP_StdPeriph_Lib_V1.6.1
開發板: STM32F4 Dicovery, STM32F429-Disco
SPL 目錄架構
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
$ tree -d -L 4
.
└── STM32F4xx_DSP_StdPeriph_Lib_V1.6.1
├── _htmresc
├── Libraries
│ ├── CMSIS
│ │ ├── Device
│ │ ├── Documentation
│ │ ├── DSP_Lib
│ │ ├── Include
│ │ ├── Lib
│ │ └── RTOS
│ └── STM32F4xx_StdPeriph_Driver
│ ├── inc
│ └── src
├── Project
│ ├── STM32F4xx_StdPeriph_Examples
│ └── STM32F4xx_StdPeriph_Templates
└── Utilities
├── Media
├── ST
├── STM32_EVAL
└── Third_Party
專案規劃
看Discovering the STM32 Microcontroller 這本書後啟發的。想法整理如下:
目的:建立一個練習STM32F4開發版的專案
專案需要的資料
STM 函式庫 source code
Build code 共用的設定如toolchain、路徑、compile flag等
一些template 檔案加入開發如Makefile、linker script、config header file
最後的目錄就是這樣。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
$ tree -L 3
.
├── conf
│ ├── build.def
│ ├── Makefile.template
│ ├── stm32f4xx_conf.h
│ └── template-bared.ld
├── labs
│ └── 0_led
│ ├── led.c
│ ├── led.ld
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── stm32f4xx_conf.h
├── libraries
│ ├── readme.txt
│ └── STM32F4xx_DSP_StdPeriph_Lib_V1.6.1
├── LICENSE
└── README.md
請注意SPL可能會因為下載版本不同,變數宣告、常數宣告、和檔案名稱路徑可能不同造成編譯失敗,這時候就當組裝作業自己解決吧。
Makefile撰寫
共用變數
這邊我們需要一個共用的設定,在實習的時候直接include。詳細說明如下,懶得看的可以直接看檔案內容 。
1
TOOL_CHAIN_PREFIX = arm-none-eabi
路徑設定
我們需要定位 專案的最頂端位址才能設定其他路徑的相對位址
除了您自己的檔案,ST 提供的函式庫和ARM的CMSIS在開發都會用到
1
2
3
4
5
PRJ_ROOT ?= ..
LIB_DIR = $( PRJ_ROOT) /libraries/STM32F4xx_DSP_StdPeriph_Lib_V1.6.1/Libraries
STM_DIR = $( LIB_DIR) /STM32F4xx_StdPeriph_Driver
CMSIS_DIR = $( LIB_DIR) /CMSIS
LDSCRIPT ?= $( PRJ_ROOT) /conf/bared.ld
1
PLATFORM = STM32F429_439xx
1
2
3
SPL_INC = $( STM_DIR) /inc
CMSIS_COMMON_INC = $( CMSIS_DIR) /Include
CMSIS_STM32_INC = $( CMSIS_DIR) /Device/ST/STM32F4xx/Include
1
OUT_DIR = $( PRJ_ROOT) /build
除非你要自己從flash搬資料到RAM、設定ISR vector、RCC等,不然一定會用到start up 檔案和system檔案。start up 檔案在SPL中有很多範本,我們使用了gcc_ride7這個版本,原因是其他的都沒有gcc這個字眼。
1
2
CMSIS_STARTUP_SRC = $( CMSIS_DIR) /Device/ST/STM32F4xx/Source/Templates/gcc_ride7/startup_stm32f429_439xx.s
CMSIS_SYSTEM_SRC = $( CMSIS_DIR) /Device/ST/STM32F4xx/Source/Templates/system_stm32f4xx.c
SPL提供assertion,使用USE_FULL_ASSERT打開。打開以後需要自行實作函數void assert_failed(uint8_t* file, uint32_t line)。
1
2
3
4
5
BUILD_MODE = DEBUG
ifeq ($(BUILD_MODE), DEBUG)
CFLAGS += -DUSE_FULL_ASSERT -g3
endif
STM32F4使用Cotex M4。題外話,對於toolchain有興趣的可以用arm-none-eabi-gcc -Q --help=target查詢有支援哪些平台。
1
ARCH_FLAGS = -mthumb -mcpu= cortex-m4
Compile flag分為
增加嚴格的錯誤檢查
設定include 路徑
叫toolchain不要用使用內建的函式庫如libc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
LDFLAGS += -T$( LDSCRIPT) $( ARCH_FLAGS)
CFLAGS += $( ARCH_FLAGS)
CFLAGS += -I. -I$( SPL_INC) -I$( CMSIS_COMMON_INC) -I$( CMSIS_STM32_INC)
CFLAGS += -D$( PLATFORM) -DUSE_STDPERIPH_DRIVER $( FULLASSERT)
CFLAGS += -Wall -Werror -MMD -std= c99
CFLAGS += -fno-common -ffreestanding -O0
專案Makefile template
這邊直接把LED閃滅的Makefile拿來當template,詳細說明如下,一樣懶得看的可以去這邊 看檔案內容。
產生的binary 檔名、定位專案的最頂端位址、並且載入前面 的設定檔。
1
2
3
TARGET = led
PRJ_ROOT = $( shell cd ../../ ; pwd )
include $(PRJ_ROOT)/conf/build.def
除了前面前面 提到的start up檔案、system檔、還有你自己的程式碼外,根據你的需求,還會需要SPL的驅動程式。這個專案我們需要GPIO和RCC (reset clock control)這兩個部份。一個是用來控制LED、另外一個用來計算時間產生以控制閃滅。
1
2
3
4
SRCS = $( CMSIS_STARTUP_SRC) $( CMSIS_SYSTEM_SRC)
SRCS += $( STM_DIR) /src/stm32f4xx_gpio.c
SRCS += $( STM_DIR) /src/stm32f4xx_rcc.c
SRCS += led.c
上面的是source檔案,但是我們編譯需要把source檔案轉成object檔案並且存在./build目錄下。
1
2
3
4
C_OBJS = $( patsubst %.c, %.o, $( SRCS)) # translate *.c to *.o
OBJS = $( patsubst %.s, %.o, $( C_OBJS)) # also *.s to *.o files
OUT_OBJS = $( addprefix $( OUT_DIR) /, $( OBJS))
不要被符號嚇到,說明如下
* 產生build/led.bin檔,前提是上面的object 檔案都編譯完成
* 產生方式
* 叫gcc 從前面的object檔案中,透過led.ld linker script產生出build/led.elf、build/led.map (debug用)
* 從build/led.elf產生build/led.bin
* 從build/led.elf產生build/led.list (debug用)
1
2
3
4
5
$(OUT_DIR)/$(TARGET).bin : $( OUT_OBJS )
$( TOOL_CHAIN_PREFIX) -gcc -Wl,-Map= $( OUT_DIR) /$( TARGET) .map,-T$( TARGET) .ld -nostartfiles \
$( CFLAGS) $( OUT_OBJS) -o $( OUT_DIR) /$( TARGET) .elf
$( TOOL_CHAIN_PREFIX) -objcopy -Obinary $( OUT_DIR) /$( TARGET) .elf $@
$( TOOL_CHAIN_PREFIX) -objdump -S $( OUT_DIR) /$( TARGET) .elf > $( OUT_DIR) /$( TARGET) .list
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
$(OUT_DIR)/%.o : %.s
@mkdir -p $( dir $@ )
$( TOOL_CHAIN_PREFIX) -gcc -c $( CFLAGS) $< -o $@
$(OUT_DIR)/%.o : %.c
@mkdir -p $( dir $@ )
$( TOOL_CHAIN_PREFIX) -gcc -c $( CFLAGS) $< -o $@
可以下make flash燒錄。使用openocd的原因是因為st-flash偶爾會有寫燒錄完成但是實際上沒有燒進去的情況
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
flash : $( OUT_DIR ) /$( TARGET ) .bin
openocd -f interface/stlink-v2.cfg \
-f target/stm32f4x.cfg \
-c "init" \
-c "reset init" \
-c "stm32f2x unlock 0" \
-c "flash probe 0" \
-c "flash info 0" \
-c "flash write_image erase $< 0x8000000" \
-c "reset run" -c shutdown
1
2
clean :
rm -fr $( OUT_DIR) gdb.txt
第一支程式: LED閃滅
Linker script 和 start up檔案
Linker script
linker script (全文 ),這個script是從成大課程作業 修改的,簡單解釋如下
有兩塊記憶體,一個是FLASH一個是RAM,FLASH 不可寫入。
那些.text、.data、.bss就不解釋了。我們這次關注下列的symbols
_sidata_sdata_edata_sbss_ebss_estack
Start up檔案
上面的這些symbol,可以對照 這邊的start up 程式碼中的reset_handler,可以發現:
搞定.bss和.data後,接下來start up會去呼叫systemInit ,而systemInit就在system_stm32f4xx.c裏面。設定完系統後就是你寫的程式碼main 上場了。
start up 檔案剩下的部份就是.isr_vector ,可以想像成一個function pointer陣列(除了最開始的stack pointer,注意stack pointer初始值也是在linker script中設定的)。
另外一個要注意的是start up source code的順序和放在記憶體的順序不一致,真正在記憶體的順序請參考linker script 。
GPIO API
設定順序如下
看開發版手冊 找出要控制燈號的GPIO
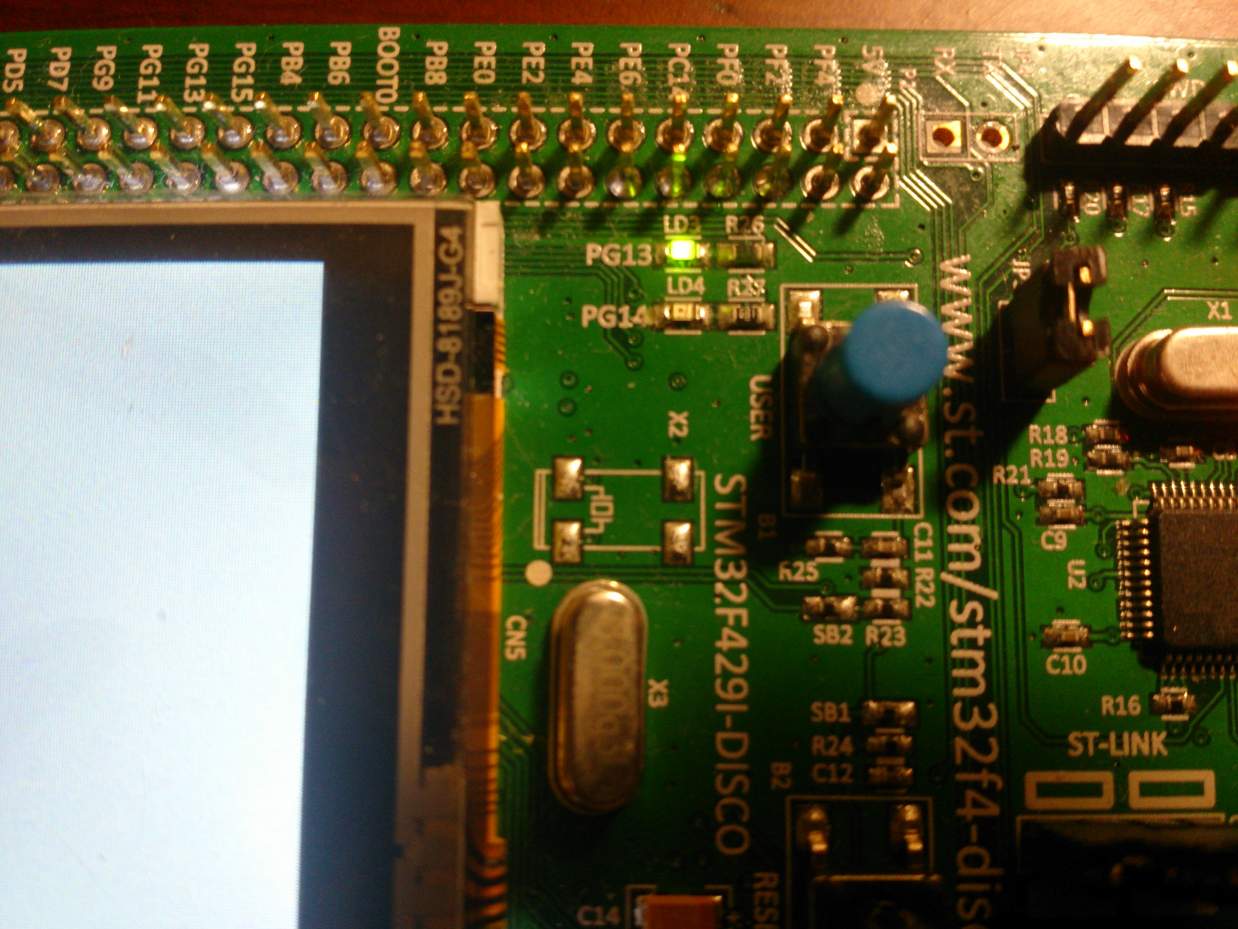
我程式就是輪流點亮點滅LED 3和LED 4,手冊上說是GPIO G的第13和14腳位
打開GPIO的clock(猜測嵌入式系統的電耗考慮,沒再用的設備都不開clock省電)
設定GPIO腳位的為輸出頻率為2MHz
GPIO設定 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
void setupLED ( GPIO_InitTypeDef * LED_InitStruct )
{
/* Setup LED GPIO */
RCC_AHB1PeriphClockCmd ( RCC_AHB1Periph_GPIOG , ENABLE );
GPIO_StructInit ( LED_InitStruct );
LED_InitStruct -> GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_13 | GPIO_Pin_14 ;
LED_InitStruct -> GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_OUT ;
LED_InitStruct -> GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_2MHz ;
GPIO_Init ( GPIOG , LED_InitStruct );
}
輸出資料到GPIO範例 1
GPIO_WriteBit ( GPIOG , GPIO_Pin_13 , 1 );
Timer ISR
要做的是
設定timer interrupt 出現的週期,設定成nano second的程式碼如下
1
2
3
4
/* Setup timer interrupt interval to nano second */
if ( SysTick_Config ( SystemCoreClock / 1000 )) {
while ( 1 ); /* Trap here if failed */
}
time out的ISR,基本上就是計數counter加上busy waiting而已
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
static __IO uint32_t g_timeToWakeUp ;
void sleep ( uint32_t nSec )
{
g_timeToWakeUp = nSec ;
/* Busy waiting */
while ( g_timeToWakeUp != 0 );
}
程式碼
這邊的assertion 實作單純是一個無限迴圈,當assertion失敗就會陷入這個迴圈。這時候用除錯器就可以找到出現assertion的行號了。
寫了以後開始修改程式碼或Makefile直到編譯過以後才針對程式行為除錯。
led.c 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
#include "stm32f4xx_conf.h"
#include <stm32f4xx.h>
#include <stm32f4xx_gpio.h>
/* A Led blink lab for STM32 Discovry Disco *
* Based on: *
* Discovering the STM32 Microcontroller by Geoffrey Brown. */
void setupLED ( GPIO_InitTypeDef * LED_InitStruct );
void sleep ( uint32_t nSec );
int main ( int argc , char ** argv )
{
static int LEDVal = 0 ;
GPIO_InitTypeDef LED_InitStruct ;
/* Setup LED */
setupLED ( & LED_InitStruct );
/* Setup timer interrupt interval to nano second */
if ( SysTick_Config ( SystemCoreClock / 1000 )) {
while ( 1 ); /* Trap here if failed */
}
/* Blinking LED3 and LED4 */
while ( 1 ) {
GPIO_WriteBit ( GPIOG , GPIO_Pin_13 , LEDVal );
GPIO_WriteBit ( GPIOG , GPIO_Pin_14 , ! LEDVal );
sleep ( 250 );
LEDVal = ! LEDVal ;
}
return 0 ;
}
void setupLED ( GPIO_InitTypeDef * LED_InitStruct )
{
/* Setup LED GPIO */
RCC_AHB1PeriphClockCmd ( RCC_AHB1Periph_GPIOG , ENABLE );
GPIO_StructInit ( LED_InitStruct );
LED_InitStruct -> GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_13 | GPIO_Pin_14 ;
LED_InitStruct -> GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_OUT ;
LED_InitStruct -> GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_2MHz ;
GPIO_Init ( GPIOG , LED_InitStruct );
}
static __IO uint32_t g_timeToWakeUp ;
void sleep ( uint32_t nSec )
{
g_timeToWakeUp = nSec ;
/* Busy waiting */
while ( g_timeToWakeUp != 0 );
}
/* ISR for system tick */
void SysTick_Handler ( void )
{
if ( g_timeToWakeUp != 0x00 ) {
g_timeToWakeUp -- ;
}
}
/* Trap here for gdb if asserted */
void assert_failed ( uint8_t * file , uint32_t line )
{
while ( 1 );
}
比較有趣的是int LEDVal = 0;一定要宣告成static,否則LED完全沒反應。在網路上請教似乎和進出ISR的時候context備份有關係,這部份有空再找時間了解一下,這次先跳過。
更新,後來測試不管是沒有static,把static改成volatile,都出現第一次燒錄行為不正常,多燒幾次又正常的情況。需要再重新釐清。
燒錄和測試
1
2
3
4
5
STM32F429-Discovery-Disco-Pratice/labs/0_led$ make
arm-none-eabi-gcc -c -DUSE_FULL_ASSERT -g3 -mthumb -mcpu=cortex-m4 -I. -I../../libraries/STM32F4xx_DSP_StdPeriph_Lib_V1.6.1/Libraries/STM32F4xx_StdPeriph_Driver/inc -I../../libraries/
...
arm-none-eabi-objcopy -Obinary ../../build/led.elf ../../build/led.bin
arm-none-eabi-objdump -S ../../build/led.elf > ../../build/led.list
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
STM32F429-Discovery-Disco-Pratice/labs/0_led$ st-flash write ../../build/led.bin 0x8000000
2016-07-25T11:31:28 INFO src/stlink-common.c: Loading device parameters....
2016-07-25T11:31:28 INFO src/stlink-common.c: Device connected is: F42x and F43x device, id 0x10036419
...
enabling 32-bit flash writes
size: 11596
2016-07-25T11:31:28 INFO src/stlink-common.c: Starting verification of write complete
2016-07-25T11:31:29 INFO src/stlink-common.c: Flash written and verified! jolly good!
以下是LED點亮結果
參考資料